Describe the Microscopic Structure of Bone and Cartilage
Bone and cartilage are types of connective tissues in the body. It is the nature of the matrix that defines the properties of these connective tissues.

Cartilage And Bones Anatomy Bones Structure Of Bone Medical Anatomy
Images of histological features of hyaline cartilage.

. Bone markings depend on the function and location of bones. Microscopic Structure of Bone Data Table 3. In the joints of the body cartilage covers the ends of the bones and acts as a shock.
As noted earlier there are two types of bone. The osseous tissue is a single component of bone but also may contain other components like blood bone marrow cartilage adipose tissue nervous tiss. Hyalos is the Greek word for glass which describes the appearance of this type of connective tissue translucent blueish-white and shiny.
Cartilage is the simple structure made up of connective tissue which is soft and are useful in providing flexibility to the joints and also protect from the external and internal shocks. SlideShare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance and to provide you with relevant advertising. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone.
Cartilage is located in very specific places usually between two bones. Flat bones consist of two layers of compact bone surrounding a layer of spongy bone. Compact bone and spongy bone.
Cartilage and Bone are specialised forms of connective tissue. Cartilage is made of chondrocytes created from chondroblasts that are isolated in spaceschambers called lacunae through a ground substance of water and sugar. Cartilage is not innervated and therefore relies on diffusion to obtain nutrients.
If you look at compact bone under the microscope you will observe a highly organized arrangement of concentric circles that look like tree trunks. A Describe the differences you observed between the fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage slides. Hyaline cartilage is made of collagen and has a distinctive glassy appearance.
Bronchial tubes or airways. Bone and Cartilage Descriptions Questions. The cartilage is a dense sponge-like matrix of collagen fibers located throughout the body.
It is a firm tissue but is softer and much more flexible than bone. Water Collagen Fibers Mineral Salts Calcification Hardening of bone tissue by the deposition of mineral salts in the collagen fiber of the matrix Hardness and Flexibility Hardness Provided by the crystallized mineral salts Flexibility. They are both made up of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix.
Needle-like threads of spongy bone. Bones are the complex structure made up of connective tissues which are hard and are helpful in providing protection shape to the body. Bone is a connective tissue containing matrix composed of calcium phosphate and other minerals.
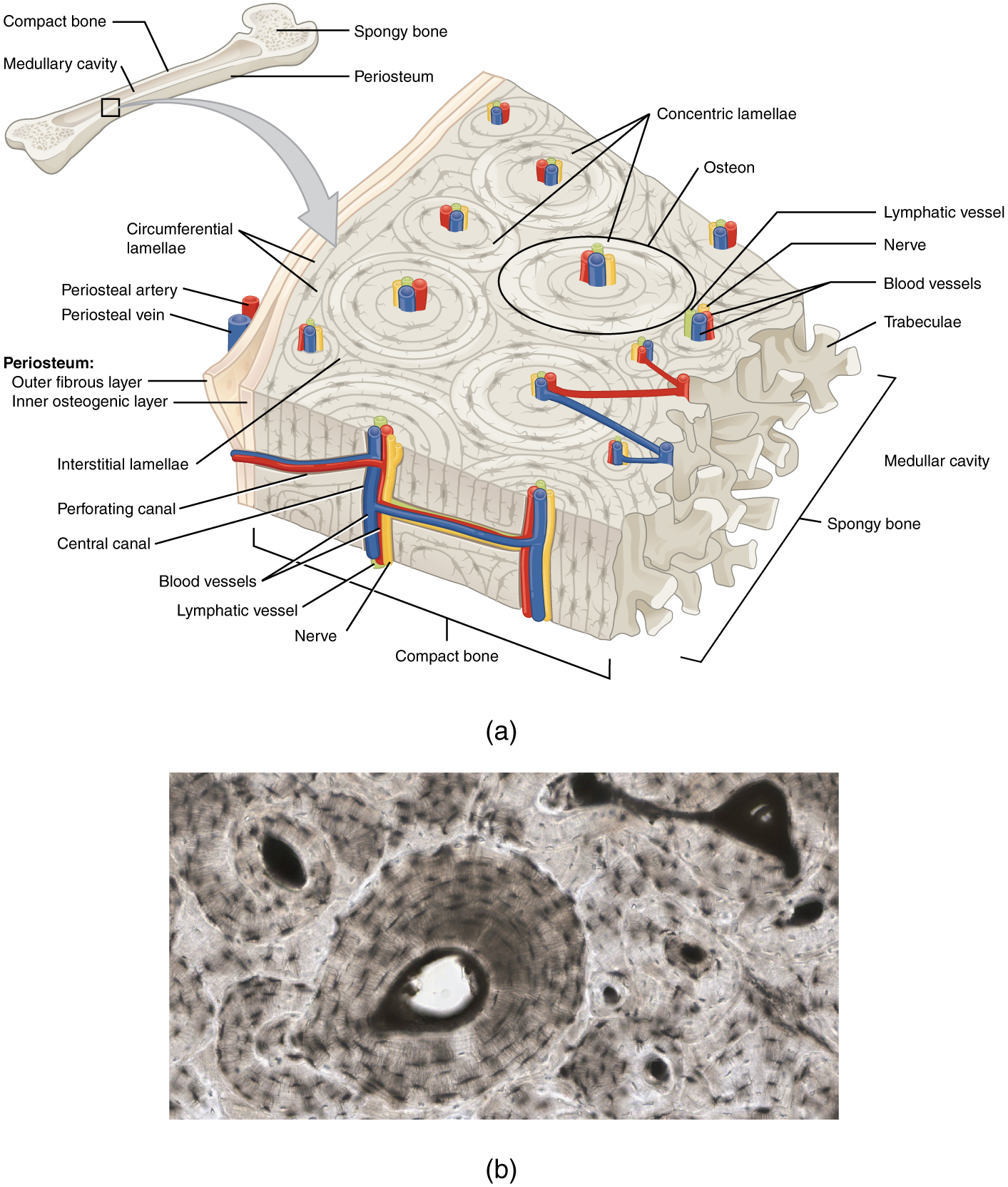
Articulations are places where two bones meet. Microscopic structure of bone and cartilage Cartilage is more. The microscopic structure of compact bone is centered around the osteon or Haversian system.
Microscopic Structure of Bone and Cartilage. Now lets take a piece of bone and cut it in half and see what it looks like on the inside. Hyaline cartilage is usually only 2 4 mm thick all cartilage must be thin as there is no vascularization in this tissue type and nutrients and oxygen must be obtained.
Cartilage has widely spaced cells. Cartilage is formed of tiny cells called chondrocytes and is surrounded by a thin transparent membrane. Ends of the ribs.
Cartilage is a connective tissue found in many areas of the body including. An osteon os-te-on is composed of a central canal containing blood vessels and nerves surrounded by the lamellae singular lamella concentric layers of bone matrix. Cartilage is a connective tissue found in various parts of the adult skeleton including all joints between bones and structures which is deformable as well as strong eg.
Microscopic Structure of Bone Osseous Tissue Another name for bone tissue Bone is a connective Tissue Widely spread cells Matrix. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways. When viewed microscopically compact bone is formed of a number of subunits called osteons.
Cartilage is thin avascular flexible. The combination of the ground substance and fibers make up a structure known as the matrix of cartilage. View the full answer.
We have 3 types of cartilage tissue. 13 rows Cartilage is a soft elastic and flexible connective tissue that protects the bone from rubbing. This causes it to heal very slowly.
Here we basically have a cross section of a piece of bone. Discuss the structural classification of exocrine glands. Cartilage by comparison is not as hard and rigid as bone and is present in areas of the body like the ear nose and joints.
The elbows knees and ankles ends of the ribs Between the vertebrae in the spine ears and nose Bronchial tubes or airways. Cartilage is made up of specialized cells called chondrocytes. Between the vertebrae in the spine.
A Cartilage resembles ordinary connective tissue in the sense that the cells in it are widely separated by a considerable amount of intercellular material or matrix. If you continue browsing the site you agree to the use of cookies on this website. In fibrocartilage you can see the fibers and appear more detailed thickerlarger unlike hyaline which seems denser making them lighter in color.
The bone cells are located in small spaces in the lamellae called lacunae. Compare the structure of the three major types of cartilage tissue. The most common form of cartilage is hyaline cartilage.
Discuss and compare the microscopic anatomy of bone and cartilage tissue. It has an appearance similar to that of the brain and the spinal cord. It is weaker than bone but it is flexible and can recover quickly.
Concentric layers of calcified matrix lamellae surround the osteon which contains blood and lymph vessels and nerves. It is a solid but semi-rigid connective tissue. Ends of long bones.
The outer surface of bone except in regions covered with articular cartilage is covered with a fibrous membrane called the periosteum. Each group of concentric circles each tree makes up the microscopic structural unit of compact bone called an osteon this is also called a Haversian. A long bone has a hollow cavity filled with bone marrow which is richly supplied with blood vessels.
- Instructor All right so were going to be talking about the microscopic structure of bone and in particular were going to be talking about what is called the haversian system. The elbows knees and ankles. Joints between bones eg.
A bone is hard tissue that forms the skeletal structure of the body. The cells are connected to the other cells and the osteon by small canals called. The bone is surrounded by a connective tissue called periosteum by which muscles and tendons are attached to the bone.
Give examples of each. Diffen Science Biology Anatomy. Microscopic structure of bone and cartilage The microscopic structure of cartilage consists of many collagenous fibers embedded in a firm gel rather than a calcified matrix.
Describe the microscopic structure of compact bone.

𝐔𝐧𝐢𝐭 𝟏 𝐇𝐁𝐘 𝐌𝐢𝐜𝐫𝐨𝐬𝐜𝐨𝐩𝐢𝐜 𝐒𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐁𝐨𝐧𝐞 𝐂𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐖𝐤 𝟐 𝟑 Flashcards Quizlet
Comments
Post a Comment